Planning and operation
General info
The wetland
At the west coast of Thermaikos gulf extends one of the most
important wetlands in Greece. Starting from Thessaloniki and heading
west to find Kalohori Lagoon, the estuary of Gallikos river, Axios
delta, the estuary of Loudias, the delta of Aliakmonas river and the
salt pans of Alyki Kitros. It is a large complex wetland system with
a total surface area of around 33000 ha. The high biological
diversity, coupled with the existence of rare and protected species
of flora and fauna, support the site’s internationally recognition.
The wetland is one of the 10 Greek Ramsar Wetlands; parts of the
wetland area are included in the Natura 2000 Network (SPA GR 1220010
and SCI GR 1220002) protected by international conventions, EU
Directives and National Legislation.
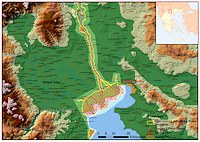
Aliakmonas and Axios Rivers
The main rivers are Aliakmonas and Axios. Aliakmonas is the largest
Greek river with a length of 350 km. The river’s headwaters are
located in the mountains of Grammos and Voio, while its estuary is
in the southern part of the Thermaikos Gulf, where it forms an
extensive delta. In mythology Aliakmonas river was a riverine deity
and according to Hesiod was the son of Ocean and Tithys. An
artificial lake created by a regulatory barrier that receives water
from three hydropower dams regulates the flow of the river.
Axios is the second longest
river in Greece with a total length of 320 km, of which 76 km belong
to Greece. The river headwaters are located in F.Y.R.O.M, and
discharges into Thermaikos Gulf. Around 95% of the river basin
belongs to F.Y.R.O.M. There are 13 dams along the riverbed, of which
twelve are on his tributaries in F.Y.R.O.M. In 1934, a river
diversion took place, in order to avoid the blockage of Thessaloniki
port due to extreme sedimentation process. New fertile areas were
formed for cultivation and a new delta established in the today’s
position.
Management Authority
of the National Park
The Axios Management
Authority is responsible for an area of 33.000 ha. The area includes
the lower reaches of four rivers and their estuaries (Gallikos,
Axios, Loudias, Aliakmonas), the Kalohori lagoon and the salt
marshes of Alyki Kitros. A Visitor Information Center is in
operation since 1997, in the town of Chalastra.
Reproduction
The spawning of the mussels takes place during late autumn till early spring. The farmers put the spat collectors during middle winter.
Settlement
 The
mussel larvae live as meroplankton for one-two months and after
metamorphosis are settled on spat collectors.
The
mussel larvae live as meroplankton for one-two months and after
metamorphosis are settled on spat collectors.
Spat growth
The spat after its settlement grows up to a length of 2-3 cm on the collectors for 3-5 months, depending on the environmental conditions of each year. At the time that spat reaches this length (2-3 cm), the operator uses it to prepare new socks. This is the first thinning procedure.
Growth
 The mussels grow for the next three months in the same socks until
late summer (August) where a new (second) thinning procedure takes
place. Depending on the environmental conditions/toxic
algae/microbial load, a new one (third) thinning procedure may
occur. Aeration (poles) or sinking (longlines) process is needed,
when the epibionts have to be removed.
The mussels grow for the next three months in the same socks until
late summer (August) where a new (second) thinning procedure takes
place. Depending on the environmental conditions/toxic
algae/microbial load, a new one (third) thinning procedure may
occur. Aeration (poles) or sinking (longlines) process is needed,
when the epibionts have to be removed.
Harvest
 The
harvest takes place when the mussels overreach the length of 5 cm
after a total average period at least of 8 months since
reproduction. The mussels are transported as socks or as 20 kg bags to the
appropriate vehicles for the markets.
The
harvest takes place when the mussels overreach the length of 5 cm
after a total average period at least of 8 months since
reproduction. The mussels are transported as socks or as 20 kg bags to the
appropriate vehicles for the markets.